
Supershift EMSA
本英文及附属网页是我们美国网站的原稿内容。因为我们的中文文案常被盗用,就不准备翻译成中文了。如有任何问题,请与我们联系,谢谢理解。
After the shift bands are observed in EMSA, super shift (supershift) or Competitive EMSA (see in other section) may need for further investigating the shifted bands.
1. What is "Super shift (Supershift) EMSA"?
After the interaction of proteins and nucleic acids, an antibody is added to check if the antibody can bind to protein/DNA or protein/RNA complexes to create an even larger complex with a greater shift. This method is referred to as a super shift (supershift) EMSA, and bands with a greater shift are called supershifted bands.
2. Principle of Super Shift EMSA
The principle of Super Shift EMSA is easy understood. The binding of antibody to the protein (antigen) in the complexes of DNA/protein or RNA/protein would increase their size gteatly and causes slow or stops mobility of complexes in the gel.

While there are characteristic shifts caused by specific protein(s) binding to target nucleic acid(s), a relative change in mobility does not identify the bound protein in a shifted complex. Identification of the protein bound to the probe is frequently accomplished by including an antibody that is specific for the putative DNA-binding in the binding reaction. If the protein of interest binds to the target DNA, the antibody will bind to that protein:DNA complex, further decreasing its mobility relative to unbound DNA in what is called a "supershift".
3. When is Super Shift EMSA needed?
After regular EMSA, Super
Shift EMSA may need for (1) identifying the specificity
of protein(s)/ nucleic acid(s) interaction, or (2) for
determining the activated subunit of transcriptional
factor family in the Protein/nucleic acid complexes.
Many transcriptional factors have many subunits to bind to a same domain in different cell lines or issues. For example, human NFkB has several subunits; p65, p52, p50, c-rel and v-rel. All these subunits are able to bind to the kB domain. As conventional EMSA cannot tell subunits involving in the protein/ nucleic acid complexes, Supershift EMSA is a unique way to identify the components of protein/DNA complex in EMSA.
4. What antibodies can be used for Super Shift EMSA?
Not all of antibodies for
a specific transcriptional factor can be used for Super
Shift EMSA. The antibodies used with Super Shift EMSA
should meet these standard: 1) the domain antibody
recognized should be on the surface of protein-nuclear
acid complexes, 2) the domain on the protein-nucleotide
acid complexes should not be overlapped with interactive
area of protein-nuclear acid complexes, 3) The
antibodies used for Western blotting will not work with
Supershift EMSA because antibody will only recognize the
denatured prim structure of proteins. 4) The domain
should be on the surface of the complexes, so that the
antibody can access to bind. 5)Few
antibodies made by injecting peptides can be used for
Supershift EMSA.
5. How to do Super Shift
EMSA?
In order to get an
expecting result from Supershift EMSA, the experiment
should consider following points:
(1)
The cell or tissue extracts should have activated
proteins/factors enabled to bind to DNA or RNA probes.
6. Explanation of
Super Shift EMSA
A sample picture (picture
2) of supershift STATs EMSA from one of our publications
(Blood 1999, 93:2369-79), in which supershifted
bands can be seen clearly. Depended on types of
antibodies, supershifted band(s) cannot be observed in
EMSA gels (picture 3 from another article of ours,
JBC 1999,274:13877–85), presenting another type of
positive Supershift EMSA when polyclonal antibody was
used; 1) no shift bands are observed, 2) the shifted
bands for the protein-nuclear acid complexes is
disappeared or become weaker than that of controls, and
3) significant aggragates are in the loading wells.
Positive Supershift EMSA
can be judged by; 1) Specific shifted bands become
weaker or disappearing, but non-specific bands are not
affected, with a clear supershifted bands incuced by
antibody-protein-nuclear acid complexes when monoclonal
or peptides-immunized antibodies are used. 2) Specific
shifted bands become weaker or disappearing, but
non-specific bands are not affected, without
supershifted bands of antibody- protein-nuclear acid
complexes in the gel when polyclonal antibodies are
used. 3) In all the cases, if non-specific bands are
also disappeared or become weaker, indicating an amount
of antibodies used is too much and the experiments need
to repeat by adjusting antibody usage.
(2) Shifted bands of protein-nuclear acid complexes
must be detected in conventional EMSA.
(3) Make sure
the antibodies are enable to bind to native proteins in
protein/nucleic acid complexes.
(4) Make sure the
antibodis can be used for Supershift EMSA.
(3)
Antibodies should be added to reaction mixture after the
reaction of protein and DNA/RNA.
(4) There should be
no oxidants in reaction system.
(5) Nuclear proteins
used for EMSA are isolated with a high-salt buffer.
Higher volume of nuclear extracts may prevent the
binding of antibody to protein/nucleic acid complexes.
(6) Usually, the concentration of antibodies used
for supershift
EMSA is much higher than that used for other
immunoassays such as Western-blotting or ELISA etc.
(7) A classic Supershift EMSA includes these reactions:
1) A sample without activated target proteins (negative
sample) + labeled probes, 2) A sample with activated
target proteins + labeled probe (positive sample), 3)
positive sample + labeled probe + low dose of specific
antibody (supershift low), 4) positive sample + labeled
probe + high dose of specific antibody (supershift
high), 5) positive sample + labeled probe + low dose of
non-specific antibody (unrelated low), 6) positive
sample + labeled probe + low dose of non-specific
antibody (unrelated high).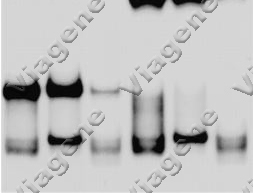
Related Products
Products/Cat#
Description
Pack
Prices
See related products
General non-radioactive EMSA kits without
probes & membrane
vary
vary
See related products
Complete non-radioactive EMSA kits with
probe & membrane
vary
vary
See related products
Non-radioactive, ready probes.
vary
vary
See related products
Custom non-radioactive EMSA probe
vary
vary
See related products
EMSA postive/negative controls
vary
vary
See related products
EMSA related chemicals and reagents
vary
vary

 客服一号
客服一号
